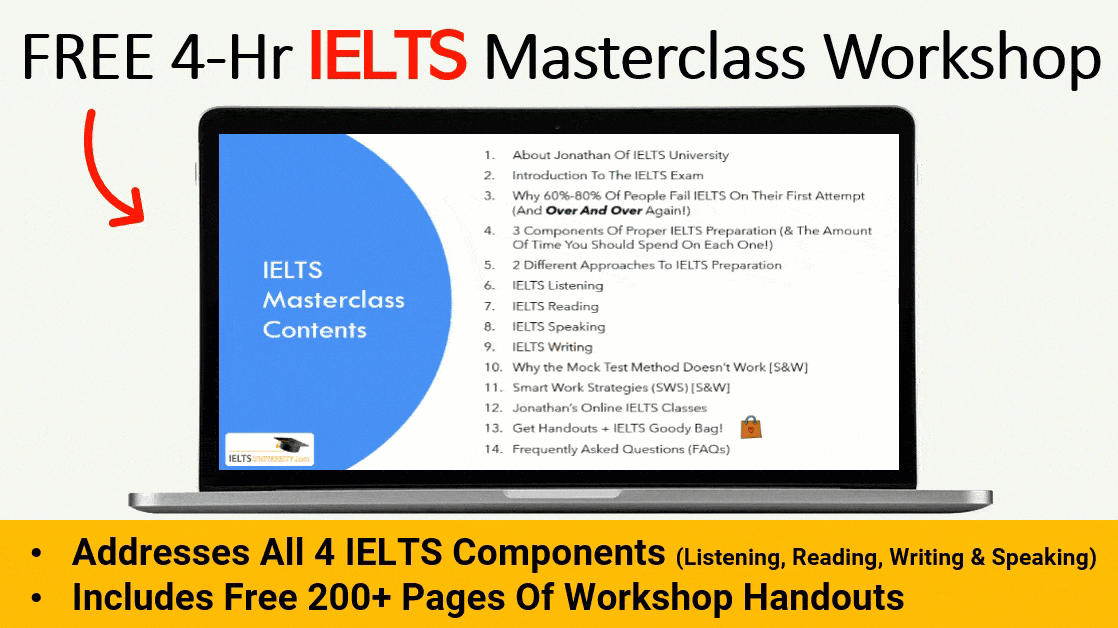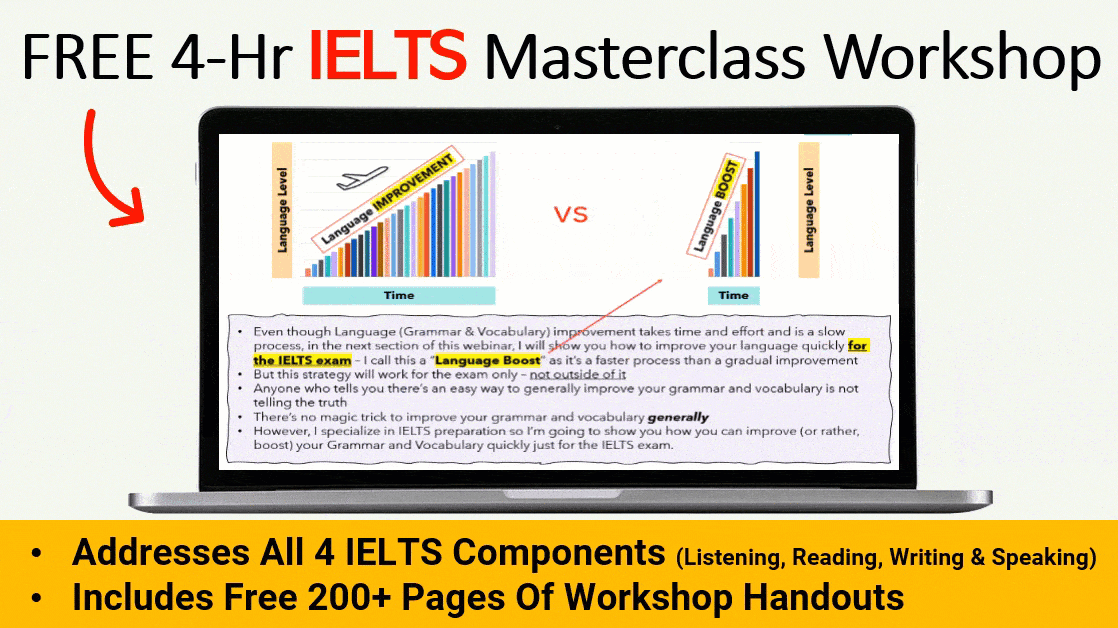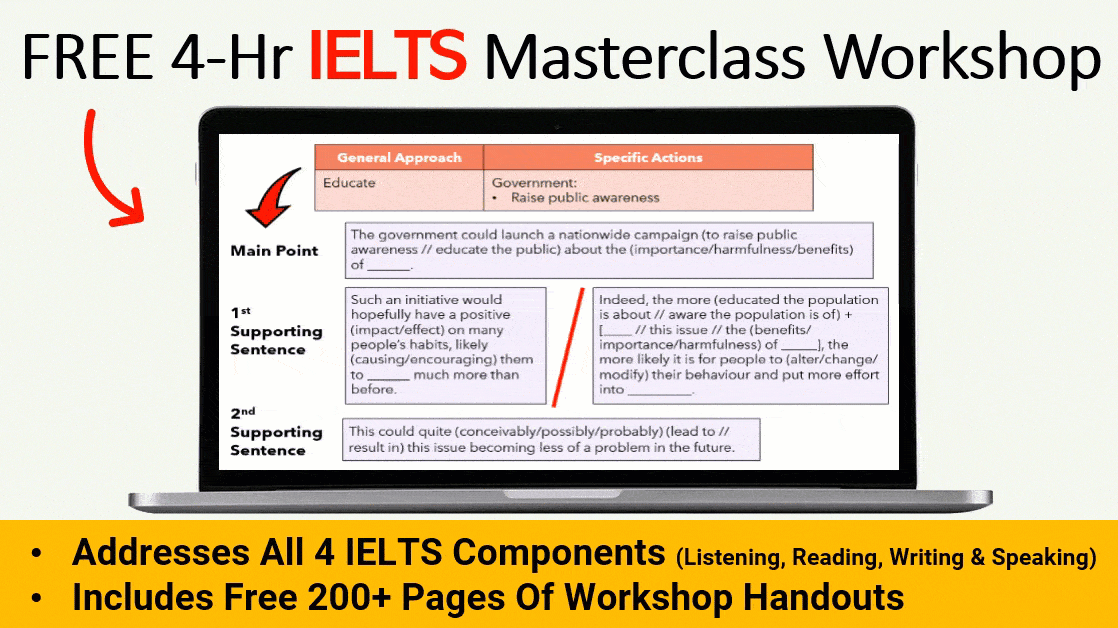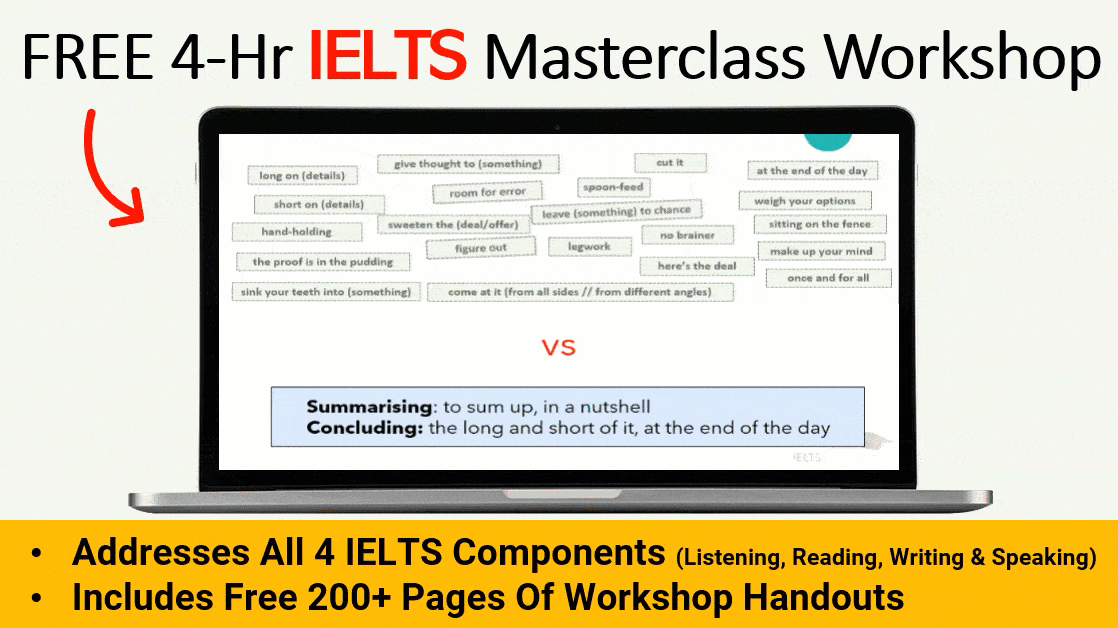
If you’re setting your sights on the IELTS general training writing task 1, you’re embarking on a pivotal section of the IELTS test. This task is distinct from the academic test and is indispensable for those looking to showcase their English proficiency for real-world, general training purposes. Whether you’re applying to immigration services, or entering the job market, this task is a key step in your journey.
As a prospective candidate, you should comprehend that the general training writing test entails drafting a letter in response to a scenario reflective of daily communications. Unlike task 2, you won’t be grappling with abstract essay prompts but instead engaging with practical situations.
The Basics of Writing Task 1 in IELTS General Training
The foundation of IELTS general writing task 1 is the art of letter writing, a skill as old as communication itself. In this part of the IELTS general training test, administered by entities like the British Council and IDP IELTS, you will apply this ancient form to modern circumstances. Your letter can take on various tones, from formal to semi-formal, or even informal, depending on the given situation.
Differences Between Academic and General Training Writing Tasks
It’s crucial to differentiate between the academic and general training paths of the IELTS test. Should you opt for the general training writing task 1, you won’t find yourself analyzing graphs or charts as you would in the academic test. Instead, you’ll navigate everyday contexts that might warrant a letter to a friend or a formal letter to an unknown entity. It’s this practical aspect that distinguishes the general from the academic.
Understanding the Task: Write a Letter
Task 1 of the general training writing test hinges on your capacity to write a coherent letter, whether it be a formal or informal letter. Much like any other section of the IELTS, it gauges your aptitude for effective communication—here, through the conventional medium of letter writing. Recalling the format for different types of letters, such as the formal structure, could prove beneficial. An examiner will assess your work with a keen eye on your approach to the letter’s purpose, the appropriateness of your language, and your ability to weave in the details mentioned in the bullet points.
Types of Letters in IELTS General Training Writing Task 1
When you’re preparing for the IELTS general training writing task, understanding the distinction between formal, semi-formal, and informal letters is crucial. Your ability to recognize these styles and apply them correctly to the task at hand can significantly influence your score.
Formal vs. Semi-Formal vs. Informal Letters
Encountering a letter in IELTS writing task 1 means you must write in a tone that matches the scenario presented. For a formal tone, consider situations where you are communicating with someone you do not know or to a professional organization. Formal letters command respectful and polite language, avoiding any contractions and colloquialisms. In contrast, informal letters are drafted with a relaxed tone, suitable when writing to a friend or relative.
Identifying the Type of Letter to Write
In the task description for general training writing task 1, you’ll find subtle cues indicating whether to write a formal or informal letter. These cues include the relationship you have with the recipient and the context of the letter. Always pay attention to the three bullet points provided; they’ll further guide the tone of your letter and its content. If asked to write a letter to a company or to address an issue formally, remember to uphold a formal style throughout your writing.
Below is a table outlining the key features you should incorporate depending on whether your letter is formal, semi-formal, or informal:
| Letter Type | Tone | Language Features | Salutation and Closing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formal | Reserved and polite | No contractions, passive voice, formal vocabulary | Dear Sir/Madam, Yours faithfully |
| Semi-Formal | Friendly yet respectful | Relaxed but polite, some contractions | Dear [Last Name], Best regards |
| Informal | Casual and personal | Direct speech, contractions, colloquial language | Dear [First Name], Best wishes/Love |
Remember, before you write the letter, decide on its nature – be it formal or informal – and ensure all elements from the tone to the sign-off align with this choice. The success of your IELTS writing task could well hinge on how effectively you differentiate between the formal and informal requirements of correspondence.
Whether you aspire to ace the IELTS general training writing task or simply wish to polish your letter-writing prowess, identifying the right tone and structure is the key to success!
Key Strategies for Excelling in General Training Writing Task 1
Gearing up for the General Training Writing Task 1 on your IELTS can be a turning point in your test preparation. A solid understanding of the exam’s expectations and a few strategic practices can elevate your written communication, taking you closer to achieving your desired band score.
Understanding the Marking Criteria
The IELTS score you seek hinges on how well you grasp the marking criteria of the general training writing test. The criteria evaluate your performance across four distinct dimensions:
- Task Achievement
- Coherence and Cohesion
- Lexical Resource
- Grammatical Range and Accuracy
In task 1, your letter should resonate with in-depth task achievement, meeting all requirements set forth in the prompt, especially addressing all parts of the task and maintaining a consistent tone throughout.
The Importance of Task Achievement and Coherence
To truly excel in the general training writing task 1, your focus should be on task achievement and the coherence of your writing. Every part of the marking criteria plays a pivotal role, but these two areas are often decisive.
Task achievement pertains to how well you fulfill the prompt. Here, the key is to cover all aspects of the task, ideally writing at least 150 words but not vastly more, to ensure depth without redundancy. Coherence, on the other hand, is about the clarity and organization of your letter. It should flow logically, with each idea connecting smoothly to the next.
Improving Lexical Resource and Grammatical Range
Enhancing your lexical resource—your range of vocabulary—is essential. A rich vocabulary allows you to express ideas succinctly and effectively without repetition. Likewise, a broad grammatical range enables you to vary sentence structure, making your writing more sophisticated and engaging.
Accurate grammar can make or break your ielts score. To avoid losing marks for basic errors, proofread your work for accuracy and strive to use a variety of grammatical constructions.
As you prepare for your IELTS general training writing task, remember that each element of your letter contributes to your overall band score. Practice writing letters that adhere rigorously to the marking criteria, and be sure to illustrate a logical progression of ideas to secure that sought-after band score. Below is an illustrative guide to better understand the correlation between different components of your letter and the band score criteria.
Effective Letter Writing Techniques for IELTS General Training
Whether you’re a novice or an experienced writer, mastering the art of letter writing for the IELTS general training writing test is crucial for achieving a top score. Your ability to present a coherent narrative will be assessed, and this section discusses how you can finesketch this skill while staying mindful of the various nuances, such as tone and structure.
Starting and Ending Your Letter Appropriately
When you commence your task 1 letter, it’s essential to immediately make clear what your letter intends to achieve. Set the right tone – be it formal or informal – based on the scenario provided. Equally important is how you conclude your piece. A formal letter might end with “Yours sincerely,” while a letter to a friend could simply use “Best regards.”
How to Address Bullet Points Effectively
Addressing bullet points is more than ticking off a list; it’s about engaging with the content and expanding on the points provided. As you write your letter, be diligent in including all elements mentioned in the bullet points. For example, if the task specifies discussing ‘various options’, ensure you explore multiple alternatives rather than focusing on just one.
Adhering to the Minimum Word Requirement
The word limit in IELTS writing task 1 is not just a threshold but a quality marker as well. Aspiring for the upper echelon of IELTS scores means writing compellingly while respecting the 150-word minimum. Craft your content to be succinct yet substantive, aiming for a word count that adheres to the requirements and showcases your linguistic prowess.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in IELTS General Training Writing Task 1
As you gear up for the IELTS General Training Writing Task, it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes that could cost you valuable points. Your aim is not just to finish the task, but to do so effectively while avoiding these traps.
Going Under the Word Limit: Risks and Consequences
When you write an informal letter or a formal one, hitting the word count is more than just a guideline – it’s a requirement. Falling below 150 words means you’re at risk of losing marks for inadequate task achievement. Every word counts towards demonstrating your ability to elaborate on the points given.
Misinterpreting the Tone of the Letter
Selecting the correct tone for a formal or informal letter is another area where many test-takers stumble. This misstep can lead to an inconsistency between what’s expected and what’s delivered. Your letter’s tone should align with the intent specified in the prompt, so pay close attention to the details provided and adjust your language accordingly.
To circumvent these pitfalls, your preparation should include a thorough analysis of sample letters for both formal and informal scenarios. Practice parsing the cues in prompts and crafting responses that precisely reflect them. This practice will ensure consistency with the given task situations and protect you from unexpected deductions in your final IELTS score.
Sample Questions and Model Answers for Practice
As you delve into the preparation for your IELTS General Training Writing Task 1, immersing yourself in sample questions and model answers generates a robust understanding of what examiners expect. These learning materials are designed to give you a good idea of how to condense complex ideas into clear and cohesive responses. It is through the strategic analysis of these elements that you will learn to craft your letters with precision and appropriateness, directly contributing to your exam success.
Analyzing Sample IELTS General Writing Task 1 Questions
When you encounter sample questions for general training writing task 1, your objective is to discern the specific information required to fulfill the task. A key strategy is to spend no more than 20 minutes on this exercise, allowing you to manage your time efficiently under exam conditions. As you dissect these sample questions, observe the demands of the task and envision how you can align your purpose and tone to the situation presented to you.
Studying Model Answers: Key Takeaways and Strategies
Model answers are not just exemplars of what to write, but also a source of strategies that help you prepare for varied prompts. A deep dive into how these answers handle the IELTS general writing task 1 reveals the intricacies of transitioning from bullet points to full-fledged paragraphs without losing coherence or conciseness. Such practice is a step forward in attaining proficiency in addressing the exam’s requirements while showcasing a high level of grammatical control and lexical range.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the focus of the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1?
A: The focus of the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1 is to assess your ability to communicate in a personal, semi-formal, or formal style depending on the task given. You will need to write a letter responding to a specific situation or request. This task tests your ability to express ideas clearly and to use appropriate style and vocabulary.
Q: How many words should I aim to write for the IELTS Writing Task 1?
A: You should aim to write around 150 words for the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1. While there is no penalty for writing more, it’s important to write at least the required number of words to ensure you have fully answered the task without unnecessarily stretching your time, which could impact your performance in Task 2.
Q: What are some tips for achieving a high score in the General Training Writing Task 1?
A: To achieve a high score in the General Training Writing Task 1, you should focus on fulfilling the assessment criteria, which include task achievement, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, and grammatical range and accuracy. Ensuring your letter is well-structured, answers all parts of the question, uses a range of vocabulary and linking words, and has minimal spelling and grammar mistakes is key. Using a semi-formal or formal tone appropriately and practicing writing concise, clear paragraphs will also boost your score.
Q: What is the difference between the IELTS Writing Task 1 in the General Training test and the Academic test?
A: The main difference between the Writing Task 1 in the IELTS General Training test and the Academic test lies in the type of task you are required to complete. In the General Training test, you are asked to write a letter (personal, semi-formal, or formal), while in the Academic test, you are required to describe visual information (e.g., a chart, graph, or diagram). The purpose, style, and audience of the writing differ significantly between the two tests.
Q: How much time should I spend on the General Training Writing Task 1?
A: You should spend about 20 minutes on the General Training Writing Task 1. This allows enough time to plan, write, and review your letter to ensure it meets the task requirements and is as error-free as possible. Remember, Task 2 carries more weight and therefore warrants more time, specifically 40 minutes.
Q: Can handwriting affect my score in the writing section of the IELTS?
A: Yes, handwriting can impact your score if the examiner finds it difficult to read. While examiners are trained to decipher various handwriting styles, it’s important to ensure your writing is as legible as possible to avoid potential misunderstandings or inaccuracies in grading your spelling and grammar. Practicing your handwriting if it is unusually hard to read could be a worthwhile effort to improve your score.
Q: What examples can I practice with for the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1?
A: Practice examples for the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1 typically involve writing letters based on everyday situations. Examples include writing to a new employer about starting a job, writing to a friend about arranging a visit, or writing to a local council about a problem in your area. These tasks often require you to request information, explain a situation, or express needs and preferences in a semi-formal or formal style. Utilizing resources such as Cambridge University Press materials or consulting with an English teacher are effective ways to find practice examples.
Q: How are tasks allocated between the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1 and Task 2?
A: The IELTS General Training Writing section contains two tasks. Task 1 requires you to write a letter (around 150 words) in a personal, semi-formal, or formal style, depending on the scenario presented. Task 2 is more demanding and involves writing an essay (at least 250 words) in response to an argument, viewpoint, or problem. Task 2 is considered more challenging and is weighted more heavily in the assessment of your writing skills.
Q: How important is using a variety of vocabulary and grammar in the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1?
A: Using a variety of vocabulary and employing a range of grammatical structures are essential for achieving a high score in the IELTS General Training Writing Task 1. These elements fall under the ‘lexical resource’ and ‘grammatical range and accuracy’ assessment criteria, respectively. Demonstrating a wide range of vocabulary and grammatical control allows the reader to understand your letter more clearly and shows your proficiency in English, leading to a higher band score.